- Veterinary PCD & Third Party Manufacturing
- +91-9023639358
- vetnationpharma@gmail.com
Veterinary With Vetnation Pharma
Veterinary Care: A Guide to Animal Health and Welfare
Veterinary care is essential for ensuring the health, well-being, and productivity of animals. Whether it’s livestock, poultry, pets, or exotic animals, veterinarians play a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases. The veterinary industry is also vital in supporting food security and controlling zoonotic diseases, which can spread from animals to humans.
In this blog, we’ll explore the scope of veterinary care, its importance, focus areas, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to provide a complete understanding of this critical field.
What is Veterinary Care?
Veterinary care encompasses the medical treatment, prevention, and management of diseases and injuries in animals. It involves a wide range of practices, including:
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Identifying illnesses and providing medication or surgical intervention.
- Preventive Care: Vaccinations, deworming, and routine check-ups.
- Animal Husbandry: Ensuring proper nutrition, housing, and breeding practices.
- Emergency Care: Addressing urgent medical conditions and injuries.
- Research: Studying diseases and developing new treatment methods.
Importance of Veterinary Care
Veterinary care is crucial for various reasons:
- Promoting Animal Health: Prevents diseases and ensures the well-being of animals.
- Food Safety: Healthy livestock ensures the production of safe and high-quality meat, milk, and eggs.
- Controlling Zoonotic Diseases: Prevents diseases like rabies, avian flu, and brucellosis that can spread to humans.
- Supporting Livelihoods: Livestock farmers rely on healthy animals for their income.
- Companion Animal Welfare: Enhances the quality of life for pets by addressing their health needs.
Focus Areas of Veterinary Care
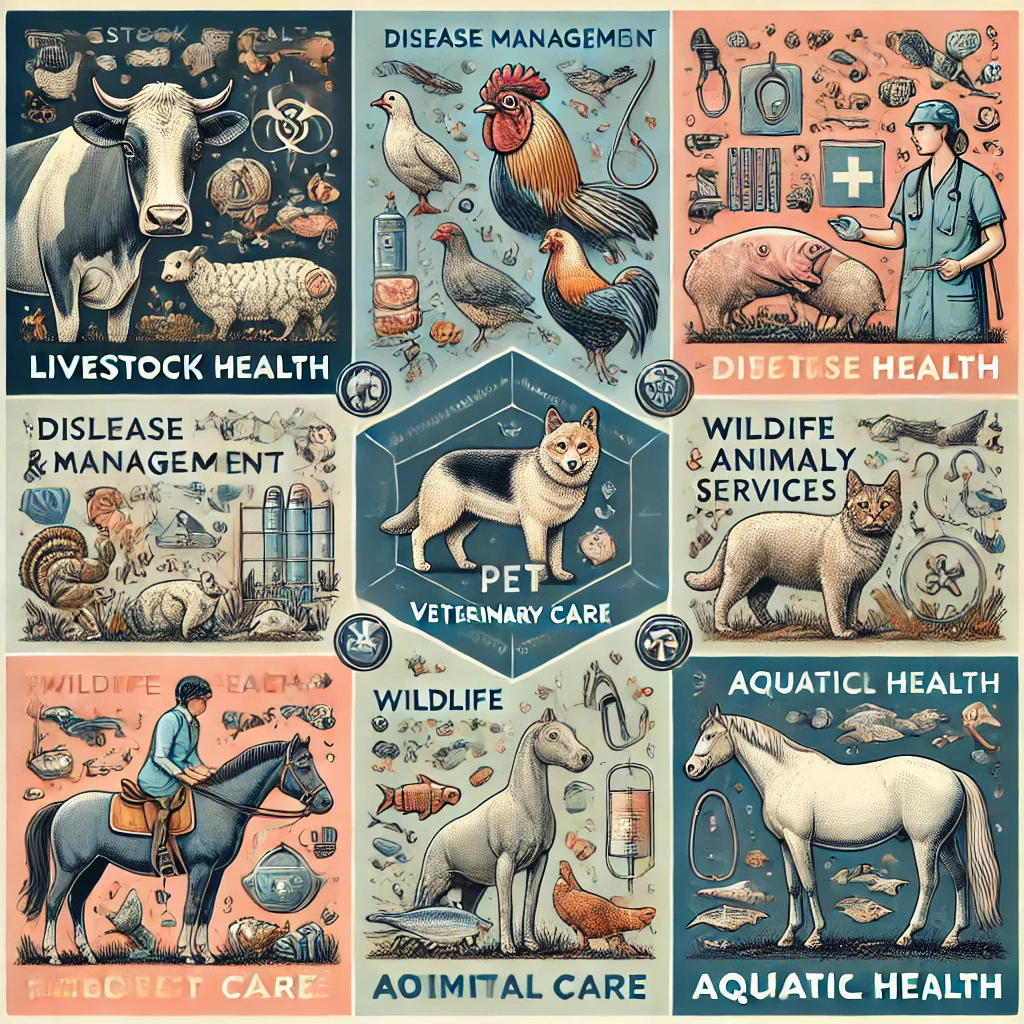

1. Livestock Health
- Focuses on the health and productivity of cattle, poultry, sheep, goats, and pigs.
- Includes disease management, vaccination, and nutritional support.
2. Pet Care
- Provides medical care for companion animals such as dogs, cats, and birds.
- Services include vaccinations, spaying/neutering, and emergency care.
3. Wildlife Veterinary Services
- Involves the care and conservation of wild and exotic animals.
- Addresses injuries, diseases, and rehabilitation in natural habitats or sanctuaries.
4. Equine Health
- Specializes in the care of horses.
- Includes treatments for lameness, colic, and hoof care.
5. Aquatic Animal Health
- Covers health management of fish and other aquatic species in fisheries and aquaculture.
- Includes water quality monitoring and disease prevention.
Veterinary Industry in India
India’s veterinary sector is growing rapidly, driven by the following factors:
- Rising Pet Ownership: Increased demand for pet care services and veterinary clinics.
- Livestock Importance: A significant contributor to the agriculture and dairy industries.
- Government Initiatives: Programs promoting animal health and vaccination campaigns.
- Global Trade: Veterinary products like vaccines and medicines are exported worldwide.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Qualifications | Ensure the vet is licensed and experienced. |
| Facilities | Check if the clinic has diagnostic and treatment equipment. |
| Specializations | Some vets focus on specific animals or conditions. |
| Location | Choose a nearby clinic for regular or emergency visits. |
| Recommendations | Look for reviews or referrals from other pet owners or farmers. |
Common Veterinary Services
Veterinary care includes a wide range of services, such as:
- Vaccinations: Protect animals from diseases like rabies, distemper, and foot-and-mouth disease.
- Deworming: Prevents parasitic infections in pets and livestock.
- Diagnostic Testing: Includes blood tests, X-rays, and ultrasounds for accurate diagnosis.
- Surgery: Performed for injuries, tumor removal, or sterilization.
- Dental Care: Ensures oral health in pets and livestock.
- Emergency Services: Addresses critical conditions like poisoning or fractures.
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccinations | Protects animals from diseases like rabies, distemper, and foot-and-mouth. |
| Deworming | Prevents parasitic infections in pets and livestock. |
| Diagnostic Testing | Includes blood tests, X-rays, and ultrasounds for accurate diagnosis. |
| Surgery | Performed for injuries, tumor removal, or sterilization. |
| Dental Care | Ensures oral health in pets and livestock. |
| Emergency Services | Handles critical conditions such as poisoning or fractures. |
How to Choose a Veterinarian?
When selecting a veterinarian for your animal, consider the following:
- Qualifications and Certifications: Ensure the vet is licensed and experienced.
- Facilities: Check if the clinic is well-equipped for diagnosis and treatment.
- Specializations: Some vets specialize in specific animals or conditions.
- Location: Choose a clinic that is easily accessible for regular visits or emergencies.
- Recommendations: Seek reviews or referrals from other pet owners or farmers.
Conclusion
Veterinary care is an essential aspect of animal health and welfare, benefiting both animals and humans. From livestock health to pet care, veterinarians provide invaluable services that contribute to better productivity, companionship, and disease prevention.

By understanding the scope of veterinary care and choosing the right services for your animals, you can ensure their long-term health and well-being.
Contact Information
Contact Vetnation Pharma if you want to know Veterinary With Vetnation Pharma or any other part of PAN India.
- Company Name: Vetnation Pharma
- Company Address: Plot no 295, Industrial area phase -2, Panchkula- 134 109, Haryana (India)
- Contact us: +91- 90236 39358
- Website: www.vetnationpharma.com/
- Write us: vetnationpharma@gmail.com
FAQs About Veterinary Care
- What is veterinary care?
Veterinary care involves diagnosing, treating, and preventing animal diseases to ensure their health and well-being. - Why is veterinary care important?
It promotes animal health, prevents zoonotic diseases, supports food safety, and improves the welfare of pets and livestock. - What services do veterinarians provide?
Vaccinations, deworming, surgeries, dental care, emergency treatment, and diagnostic tests. - How often should I take my pet to the vet?
Annual check-ups are recommended, with more frequent visits for younger, older, or sick pets. - What is the role of veterinary medicine in livestock farming?
It ensures livestock health, productivity, and supports agriculture. - What are zoonotic diseases?
These are diseases that can spread from animals to humans, such as rabies or avian flu. - Can veterinarians treat all animals?
Most treat common pets and livestock; specialists handle exotic or wildlife species. - What are the most common pet vaccinations?
Core vaccines include rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus. Additional vaccines depend on the pet’s needs. - Are there veterinary emergency services?
Yes, many clinics offer 24/7 emergency care for critical cases. - How can I ensure good health for my animals?
Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, vaccinations, and maintaining a clean environment.
